[lwptoc]
The JobKeeper scheme is currently legislated to end on 27 September 2020. On 21 July 2020, the Government announced that due to the ongoing COVID-19 crisis, the JobKeeper Payment scheme will be extended by six months until 28 March 2021, with changes to the payment rates and the entity decline in turnover eligibility test.
On 7 August 2020, the Treasurer announced further changes to increase access to the scheme, driven by the ongoing crisis and the implementation of Stage 4 business restrictions in Victoria. Relevantly, this second announcement included that from Monday 3 August 2020, the employee eligibility reference date will move from 1 March 2020 to 1 July 2020.
On 14 August 2020, the Treasurer registered a Legislative Instrument titled Coronavirus Economic Response Package (Payments and Benefits) Amendment Rules (No. 7) 2020 (the Amendment Rules). The Amendment Rules amend the Legislative Instrument containing the JobKeeper Rules to change the employee eligibility reference date from 1 March 2020 to 1 July 2020. The stated purpose of the Amendment Rules is to extend the scope of the wage subsidy support so that it also benefits employers of more recently engaged employees.
The other changes announced on 21 July 2020 and 7 August 2020 will be included in separate amendments.
Also on 14 August 2020, the ATO confirmed that it will allow employers until Monday 31 August 2020 to meet the wage condition for, and to enrol, employees who are newly eligible for JobKeeper under the 1 July 2020 eligibility test.
This article outlines the effect of the Amendment Rules. Previous Banter Blog articles summarise the operation of the current JobKeeper scheme and the proposed changes.
![]() Important
Important
The Amendment Rules only changes the eligibility reference date for employees and not for business participants and religious practitioners.
For JobKeeper fortnights ending on or before Sunday 2 August 2020, an individual was an eligible employee of their employer for a fortnight where they satisfied the following requirements:
The Amendment Rules have changed the eligibility reference date for employees for JobKeeper fortnights commencing on or after Monday 3 August 2020.
The revised reference date applies to:
The revised eligibility criteria are as follows:
The amendments allow employees who are not eligible under the former 1 March 2020 test date, but are now eligible under the 1 July 2020 reference date, to be enrolled for JobKeeper for fortnights commencing on or after 3 August 2020.
Affected employees include those who:
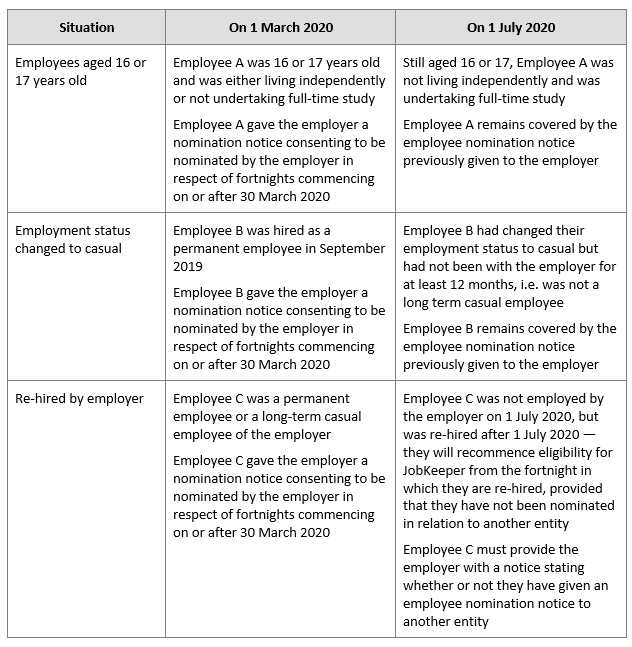
On 1 June 2019, Kym began working as a casual barista at Top Cafe. During the period of 12 months that ended on 1 July 2020, she regularly worked shifts on Friday and Saturday mornings and occasionally worked shifts on other days. Although Kym may have worked different numbers of hours each week, Kym can be considered to be a long-term casual employee of Top Cafe because, on 1 July 2020, she was employed on a regular and systematic basis for a period of 12 months.
Source: ATO fact sheet ‘Long term casual employees’ (QC 63423)
![]() Note
Note
The ATO has updated its web guidance to state that the long term casual employee test requires that the employee was employed on a regular and systematic basis for the period 2 July 2019 to 1 July 2020.
No. Individuals who satisfied the 1 March 2020 requirements under the previous law do not need to retest (and potentially lose) their eligibility under the new rules. That is, their eligibility is preserved, regardless of any change in circumstances by 1 July 2020 which would otherwise make them ineligible based on a 1 July 2020 test date.
Examples include:
HYLT Pty Ltd qualified for JobKeeper payments for four eligible employees for the JobKeeper fortnight beginning 30 March 2020 and later fortnights.
After the end of the third JobKeeper fortnight, one of the eligible employees, Rosie, left HYLT Pty Ltd due to the lack of business for HYLT Pty Ltd and to pursue another opportunity. During this later time, HYLT Pty Ltd qualified for JobKeeper payments for only three eligible employees.
On 28 July 2020, Rosie returned to HYLT Pty Ltd and resumed ongoing full‑time employment. Further, Rosie was not eligible to renominate as an eligible employee of another qualifying entity.
For JobKeeper fortnights beginning on or after 3 August 2020, despite Rosie not meeting the 1 July 2020 requirements, HYLT Pty Ltd can qualify for the JobKeeper payment in respect of Rosie as a 1 March 2020 employee under the Rules. This is because Rosie’s eligibility based on the 1 March 2020 requirements was preserved since she was an eligible employee of HYLT Pty Ltd for a JobKeeper fortnight ending on or before 2 August 2020 and she did not qualify as an eligible individual of another qualifying entity.
Source: Example 4 from the Explanatory Statement
The JobKeeper Rules require that an employer must give every eligible employee the choice to be nominated, i.e. by providing them with a nomination notice. This is commonly known as the ‘one in, all in’ rule. The Amendment Rules effectively ensure that this rule will also apply to an employer in respect of all their employees who are eligible under the 1 July 2020 test date, other than those who had already been given this choice.
The Amending Rules make changes to the nomination requirements. The former requirements effectively prevented eligible individuals from nominating for the JobKeeper scheme for more than one entity. The amendments provide an exception to this restriction. Under the exception an individual who has nominated with one entity as an eligible employee or an eligible business participant can re-nominate as an eligible employee of another entity in limited circumstances.
To re-nominate, the individual must have:
![]() Important
Important
An individual can only re-nominate as an eligible employee. They cannot re-nominate as an eligible business participant. Further, an individual cannot re-nominate if they were a religious practitioner in relation to either entity.
Example — re-nomination
Lee joins NewJob Inc on 27 June 2020 as a full time employee after leaving his former employer. His former employer qualified for JobKeeper payment in respect of Lee for the JobKeeper fortnight beginning on 30 March 2020 and later fortnights until he left in June. As Lee has left his former employer, his former employer no longer qualifies for the JobKeeper payment in respect of Lee as an eligible employee.
For JobKeeper fortnights beginning on or after 3 August 2020, NewJob Inc can qualify for JobKeeper payments in respect of Lee as an eligible employee because he satisfies the 1 July 2020 requirements. Further, Lee is not excluded from being nominated under the JobKeeper scheme because he left his former employer before 1 July 2020 and was employed by NewJob Inc on 1 July 2020.
Source: Example 2 from the Explanatory Statement
The ATO has updated its JobKeeper Employee Nomination Notice to reflect the new eligibility test date of 1 July 2020 and the re-nomination exception.
This updated nomination notice only applies to employees who are enrolled based on the new 1 July 2020 eligibility reference date.
Where all of the following apply in respect of a re-hired employee:
the employee needs to provide to the employer a notice stating whether or not they have given an employee nomination notice to another entity.
The Amendment Rules do not change any of the eligibility criteria for the employer. Relevantly, the entity must meet the wage condition in respect of employees who becomes eligible based on the new 1 July 2020 test date for a fortnight commencing on or after 3 August 2020.
Under the JobKeeper Rules — and not changed by the Amendment Rules — an employer must pay an eligible employee at least $1,500 for the relevant JobKeeper fortnight. The Commissioner has the discretion to allocate an amount paid outside of a particular JobKeeper fortnight to that fortnight, where the regular pay period is longer than a fortnight (e.g. a monthly payrun), or where it is otherwise reasonable in the Commissioner’s opinion to do so.
The ATO is allowing all employers until Monday 31 August 2020 to meet the wage condition for all new eligible employees included under the 1 July 2020 eligibility test. This covers the two fortnights from 3 August to 16 August 2020, and from 17 August to 30 August 2020.
![]() Important
Important
The blanket extension until 31 August 2020 only applies in respect of new employees added as a result of the change of the reference date. It does not apply to already enrolled employees who qualified based on the 1 March 2020 test date.
The ATO generally allows employers to enrol new eligible employees by the end of the calendar month in which they became eligible (although the wage condition must be satisfied for each fortnight subject to the Commissioner’s discretions). Consistent with this general practice, employers may enrol new eligible employees for the August fortnights by 31 August 2020.
![]() Further information
Further information
For more on the latest legislation changes, join us for our monthly online tax updates, hosted by some of Australia’s leading tax experts.
We facilitate these online and in locations across Australia (in line with current COVID-19 restrictions).
Join thousands of savvy Australian tax professionals and get our weekly newsletter.